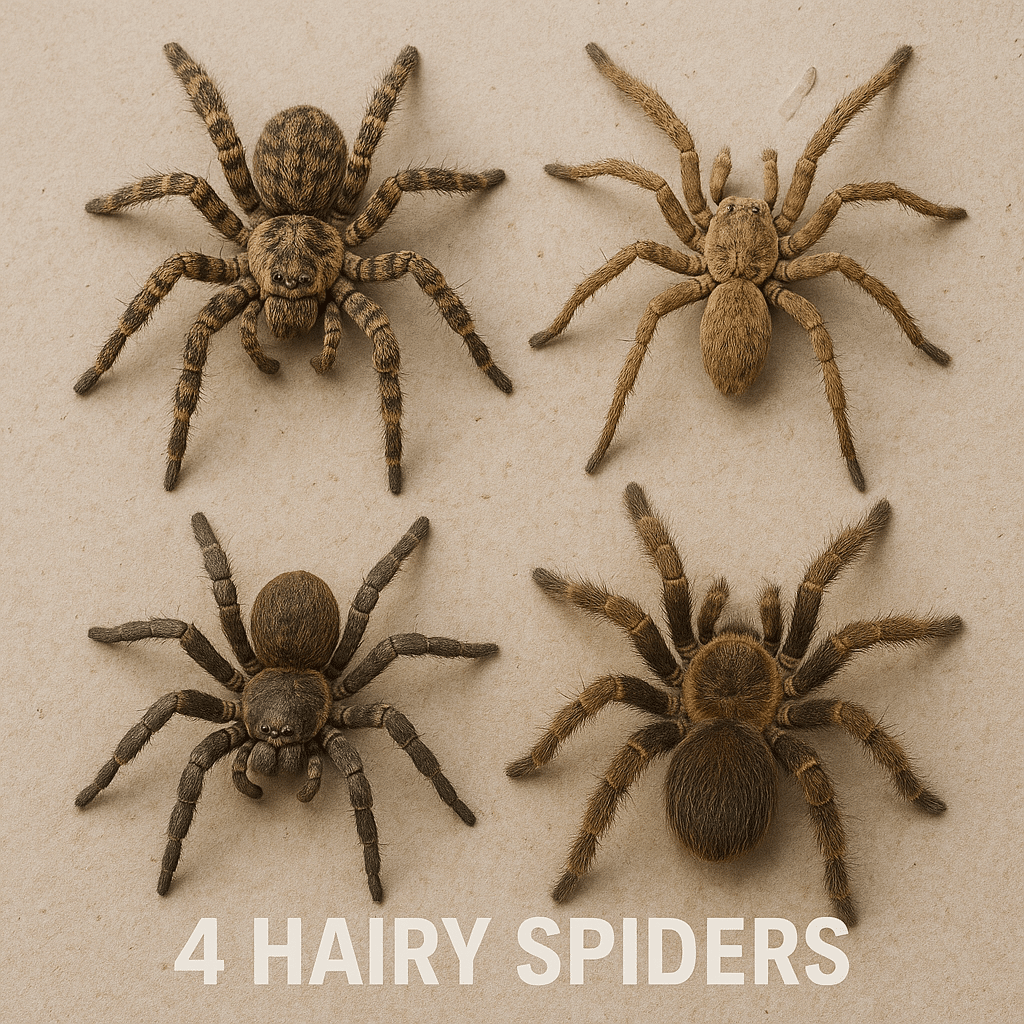
Discover Fascinating 4 Hairy Spiders Species Might Encounter
Anyone’s first experience of finding one of these 4 hairy spiders can be startling with their fuzzy body and all those fast, skipping legs. Many even shudder with the thought of spiders, let alone large and hairy ones.
Yet these eight-legged creatures play essential roles in our ecosystems. Some keep the insect population under control, others help by consuming pests that destroy crops, and many hairy spiders have generally interesting behaviours.
In this post, we’ll look at 4 types of hairy spiders you might see. We’ll discuss how to recognize them, where they live, and what to do if one wanders into your space.
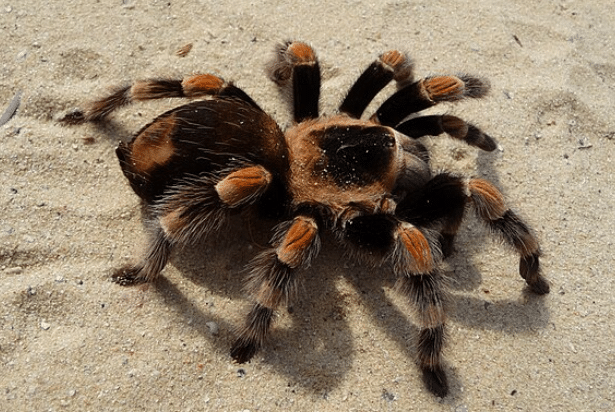
1. Tarantulas
Identification
Tarantulas are probably the best-known hairy spiders in the world. Their large bodies make them hard to overlook. Leg spans range from a mere 2 inches up to a colossal 12 inches, based on species. These spiders typically look heavy-bodied as their legs are thick and robust. Their bodies also have thick, bristly hairs in many different colors. Some species are decorated with orange markings. Others have metallic blues and still, others stick with more conservative shades of brown or black.
Most tarantulas flick hairs off of their abdomen when threatened. The sharp hairs will work into the predator’s skin or eyes as an irritant. A good reason not to go around tasting things. A few tarantulas practice this trick; others, however rely on their ability for speedy retreat to burrow or hide.
Where They Live
You can find wild tarantulas in warm regions across the globe. Many are found in the Americas, parts of Africa, and parts of Asia. They generally prefer dry, warm habitats such as deserts, scrublands, or even grasslands. Most tarantulas burrow into the ground and live in solitude. A few species will live in trees, especially in tropical regions. Tarantulas are one of the most popular pet spiders among enthusiasts.
What to Know
Truthfully, tarantulas do not bite unless they are highly threatened. A tarantula’s bite could easily feel no worse than that of a bee. Of course, those with particular allergic reactions should still beware. Never touch a wild tarantula if it makes you nervous. Typically, it is best just to observe them calmly from a distance.
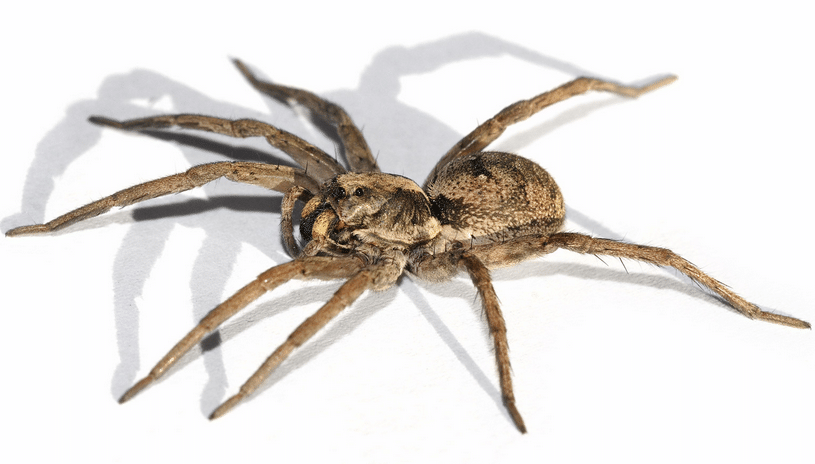
2. Wolf Spiders
Identification
Wolf spiders do not catch their prey in webs. Rather, they are active hunters who seek out food. They have muscular bodies and long legs to attain high speeds. Many species are between half an inch and 1.5 inches in body length. Some species of wolf spiders are much larger, however. Their hair is not that impressive as that of tarantula, yet you still can notice some fuzzy patches on legs. Most of them are brown or Gray, with distinctive stripes or markings upon their thorax and abdomen.
Wolf spiders have excellent vision for ground movements. Many species are active hunters at night, actively pursuing crickets, beetles, and other crawling insects. They have been called “wolf spider” because of their style of hunting by stalking and then ambushing their prey. They are quick to react and possess powerful jaws.
Where They Live
You will find wolf spiders in a variety of habitats. They are found in gardens, forests, and grasslands, and even in your yard. Most of them prefer living under the leaf litter, logs, and rocks. They also enter homes occasionally, especially during the colder months. They might be seen to run across the floor or finding shelter in dark places. They do not usually build their webs in open areas. Instead, they either run down or ambush their prey.
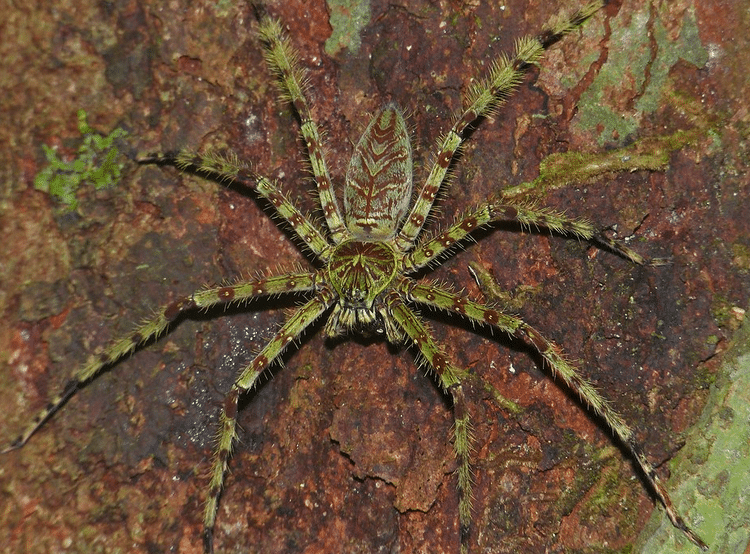
3. Huntsman Spiders (Sparassidae Family)
Identification
Huntsman spiders have crab-like legs that splay sideways. Not all huntsman spiders are that hairy, but many show fuzz along their long legs and abdomen. Their leg span can exceed 5 inches for some species and thus often make them seem quite large. Colors range from light beige to darker browns or greys. Many have patterns that enable them to blend into tree bark or foliage.
Huntsman spiders usually rest in a flat position, with their legs extended to the side. This makes them somewhat hard to spot. Their body can also be somewhat flattened, allowing them to squeeze into tight crevices.
Where They Live
You will find huntsman spiders in warmer climates around the world. Large populations reside in Australia and parts of Asia, Africa, and the Americas. They are fond of hiding in places, such as under loose bark or behind wall hangings. Since they roam at night, you may catch them scurrying across walls or ceilings. Some get indoors when they hunt or seek shelter.
What to Know
Huntsman spiders are very fast movers. Their rapid, sudden movements often alarm people. Generally, huntsman spiders do not bite unless they are trapped or otherwise provoked. A bite may hurt but is unlikely to be serious. Actually, huntsman spiders help to maintain cockroach and other insect numbers down. If they turn up in your garage or shed, you can just leave them alone to get on with their work. If you are nervous, scoop them up in a container and release them outside.
4. Trapdoor Spiders
Identification
Trapdoor spiders are mygalomorphs, just like tarantulas. They have stout bodies that have short, fine hairs. Some people can’t even see the fuzz with casual observation. Trapdoor spiders are about 1 to 1.5 inches in body length. For some species, they could be larger. They usually are colored dark brown or black so they will blend into the soil better.
Their hunting style is quite unique. They wait in burrows for a prey animal to pass close by them, then pounce out to seize a meal. Unlike tarantulas, trapdoor spiders do very little roaming in the open.
Where They Live
Trapdoor spiders build silk-lined burrows in warm or temperate regions of the world. They frequently line a “trapdoor” of silk and debris at the entrance. This covers their hideaway. They prefer loose soil where they can dig more easily. You may see evidence of their burrows in gardens, forests, or grassy areas.
What to Know
These spiders rarely leave their tunnels. Because of that, you’ll seldom see one unless you disturb its home. Some pain or swelling if spider trapdoor bites you. Serious harm is unlikely unless you have specific sensitivities. They generally avoid contact with people. So they pose little danger unless you accidentally dig one up or poke into their burrow. If you find a trapdoor spider’s hole, consider leaving it undisturbed. It quietly controls insects, largely without most people even taking notice.
Conclusion
Among all causes of deep fears, there are hairy spiders. After reading about them, you might start appreciating what they do for us. Each of those spiders has its own peculiarities and behaviours. Their presence in our world is much more helpful for us than harmful.
Being informed means that you will not freak out when you see a hairy spider. You’ll know whether it’s harmless or you require professional help. Most often, your best move is a gentle catch and release. This way, you respect nature and your home stays spider-free.
Maximum Pest Control Services
Contact Us: https://www.maximumpestcontrol.ca/contact-us/
Connect on Google: https://g.co/kgs/UDjHZyA
96R6+9J Burlington, Ontario